Stem Cells
Stem cells are the un-differentiated cells which have capacity of self renewal and differentiation. They are present in all multicellular organisms. Alexander Moximov was the Russian haematologist who postulated about stem cells.
Characteristics of stem cells
They have the capacity of
Self renewal: divide to form more stem cells
Differentiation: convert themselves to adult somatic cells
Trans differentiation: stem cell of one cell line differentiates into adult cell of other cell line
Extreme mitogenic potential: capacity to divide
Chemotaxis: migration in response to chemical stimuli
Niche & Homing: find their comfort zone and starts living there
Chemokine activity: cell to cell communication through protein molecules
Stem cells are classified on following basis
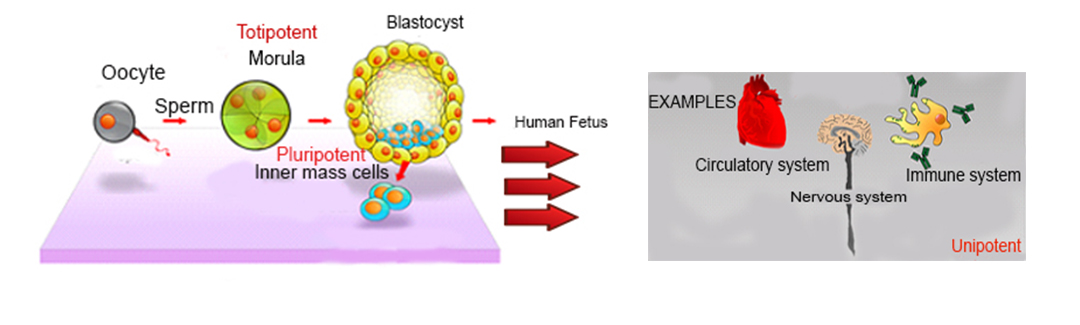
Potency: totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, oligopotent, unipotent
Chronology: embryonic stem cells (ESCs), foetal stem cells (FSCs), cord blood cells (CSCs), adult stem cells (ASCs)
Characteristics: Haemopoeitic stem cells (HSCs), Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Tissue of homing: adipose tissue derived stem cells (ASCs), bone marrow stem cells(BMSCs), skin precursor cells (SPSCs), GUT
Others: very small embryonic cells ( VSEL)
The cells best suited for clinical transfers are
Multipotent
Adult stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells
- Adipose tissue stem cells
Autologus
There are only rare indications of allogenic transfers ex: blood dyscrasias & cancers. Stem cells from bone marrow are rich in growth factors.
There are following known accessible sources of autologous adult stem cells in humans
Bone marrow, which requires extraction by harvesting, that is, drilling into bone (typically the tibia, femur or iliac crest).
Adipose tissue (lipid cells), which requires extraction by liposuction.
Blood, which requires extraction through aphaeresis, wherein blood is drawn from the donor (similar to a blood donation) after pharmacological activation of bone marrow, and passed through a machine that extracts the stem cells and returns other portions of the blood to the donor.
Tooth, menstrual blood, hair follicles, skin
Division of stem cells

Illustration showing potency of stem cells at various stages of development